Hengshi Documentation
HENGSHI SENSE Data Permission Solution
1. Introduction
1.1. Purpose of This Document
This solution mainly discusses the data permission scheme of HENGSHI SENSE, which means that in the HENGSHI SENSE system, by synchronizing the internal personnel attributes and organizational structure information of the enterprise, the data reading permissions for each user within the enterprise for business data are implemented.
The expected readers of this solution are: HENGSHI SENSE design and development personnel, and enterprise customer developers of HENGSHI SENSE.
1.2. Background
To meet customer demands of filtering data based on business system data permissions.
1.3. Glossary
| No. | Term | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Permission | The range of authority a user has over resources |
| 2 | Functional Permissions | Operational permissions a user has on the HENGSHI SENSE system |
| 3 | Data Permissions | The data set basis for calculations when a user views each report in the HENGSHI SENSE system |
| 4 | User Attributes | A part of user-defined information (user attributes/portraits, used to filter user groups, filter data), generally synchronized to HENGSHI SENSE, see 3.1 for details |
| 5 | Organizational Structure | Internal organizational structure information of an enterprise, generally in a tree-like structure, each user belongs to one or several nodes (currently, HENGSHI SENSE only supports one) |
2. Overview
2.1 Data Permission Rules
= Authorized User Group + Data Filter
2.1.1 Specifying the Authorized User Group
- By specifying specific users
- By specifying specific groups
- By specifying through user-defined attributes
2.1.2 Creation of Data Filter
- Specify constant filters in the filter
- Use user-defined attributes to filter in the filter, for example:
- table1.area = $USER.area
- table1.years_of_entry <= yeardiff($USER.entry_time, now())
2.1.3 Data Permission Rules Based on Organizational Structure
- The business data table contains fields related to organizational structure, such as department ID
- User-defined attributes that have properties related to organizational structure, such as the affiliated department ID
2.2 Objects of Data Permission Control
- Tables in data connections
- Datasets in published applications
2.3 Process Design
Design principles of processes:
- Reduce system coupling
- Avoid duplication of operations
- Use only results, avoid copying implementation logic, and changes in one party's logic require the other party to make synchronous modifications
Process:
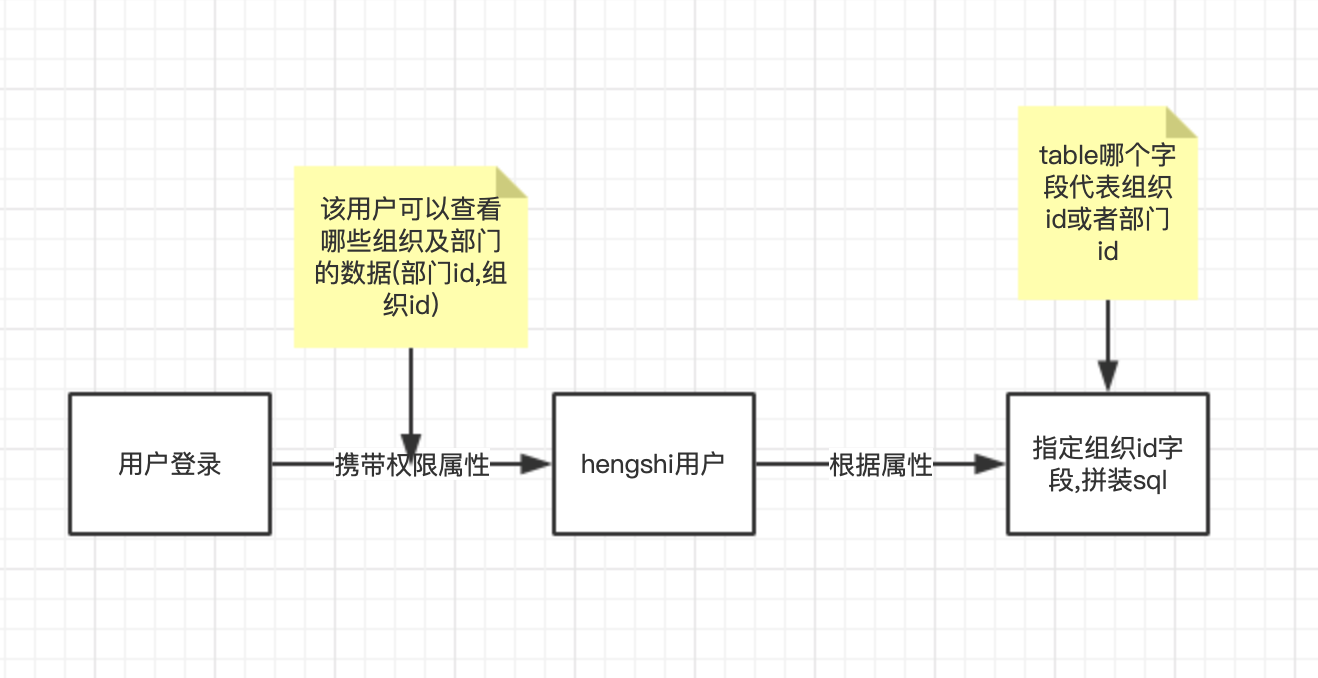Explanation of the process:
- When a user logs in, pass which permissions the user has, such as department id collection, organization id collection, or prohibited id collection.
- Hengshi will save these permissions to the user's property.
- In [Data Connection] -> [Select Data Table] -> [Permission Control], configure by specifying the organization id or department id fields in that table, and match and filter with the permission properties in the user properties.
Example 1:
Table A includes Company C, subsidiaries CC1 and CC2, and companies D and E. The organizational id field in Table A is represented as org_id. User U's accessible organization id collection includes the ids of C, CC1, CC2. Therefore, according to the permission filter, the data visible to user U is only of C, CC1, CC2.
3. Data Structure
3.1. User Attributes
Basic Information
| Parameter | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| login_name | Username | Unique/Required |
| name | Display Name | Required |
| Unique | ||
| Enabled/Disabled flag | Required (Reserved, not enabled) | |
| mobile | Mobile Number | Unique |
| Note | Can be empty (Reserved, not enabled) | |
| group_ids | List of User Group IDs | |
| role_ids | List of Role IDs | |
| {XXX} | Other custom attributes | Only supports numbers, strings, arrays (elements are numbers or strings) |
Recommended Fields for Attributes
| Parameter | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| dept_ids | List of Department IDs | Customizable name |
| org_ids | List of Organizational IDs | Customizable name |
| permit_dept_ids | List of Department IDs user has permission to access | Customizable name |
| permit_org_ids | List of Organizational IDs user has permission to access | Customizable name |
| inhibit_dept_ids | List of Department IDs user is prohibited from accessing | Customizable name |
| inhibit_org_ids | List of Organizational IDs user is prohibited from accessing | Customizable name |
Example:
{
"login_name":"zhangjunjie",
"email_verified":false,
"nickname":"Zhang Junjie",
"name":"Zhang Junjie",
"mobile":"13383338333",
"preferred_username":"zhangjunjie",
"given_name":"Junjie",
"family_name":"Zhang",
"mail":"zhangjunjie@hengshi.com",
"dept_ids":[
"1",
"2"
],
"org_ids":[
"1"
],
"permit_dept_ids":[
"1",
"2",
"3"
],//This user can access data with department identifiers (id, number, name) 1, 2, 3
"permit_org_ids":[
],
"inhibit_dept_ids":[
],
"inhibit_org_ids":[
"5",
"6"
],//This user cannot access data with organization identifiers (id, number, name) 5, 6
"role_ids":[
1,
2
],
"group_ids":[
1,
2
]
}4. Synchronization Interface
4.1. API
4.1.1 OAuth Login Interface
Return value:
{
"login_name":"zhangjunjie",
"email_verified":false,
"nickname":"Zhang Junjie",
"name":"Zhang Junjie",
"mobile":"13383338333",
"preferred_username":"zhangjunjie",
"given_name":"Junjie",
"family_name":"Zhang",
"mail":"zhangjunjie@hengshi.com",
"dept_ids":[
"1",
"2"
],
"org_ids":[
"1"
],
"permit_dept_ids":[
"1",
"2",
"3"
],//This user can access data with department identifiers (id, number, name) 1, 2, 3
"permit_org_ids":[
],
"inhibit_dept_ids":[
],
"inhibit_org_ids":[
"5",
"6"
],//This user cannot access data with organization identifiers (id, number, name) 5, 6
"role_ids":[
1,
2
],
"group_ids":[
1,
2
]
}4.1.2. DingTalk
You can customize user properties, as shown below:
4.1.3. CAS/SAML2 Login Interface
CAS/SAML2 cannot pass permission information for the time being, it is synchronized by the synchronization interface.